When we talk about the national grid, we’re diving into the lifeline of modern energy infrastructure. It’s not just some random system of wires and transformers; it’s the backbone that keeps our cities buzzing, our homes illuminated, and our industries powered. Think of it as the circulatory system of electricity, ensuring that every corner of the country gets its fair share of power. Whether you’re streaming Netflix, charging your phone, or running your business, the national grid plays a critical role in making it all happen.
Let’s be real, most people don’t think about the national grid until something goes wrong—like when the lights go out or the AC stops working on a sweltering summer day. But behind the scenes, this massive network is working tirelessly to balance supply and demand, manage energy flows, and keep things running smoothly. It’s not just about flipping a switch; it’s about maintaining a delicate equilibrium that affects millions of lives.
So why should you care about the national grid? Well, it’s more than just a technical marvel—it’s a reflection of how we generate, distribute, and consume energy. As the world shifts toward renewable energy sources and smarter grids, understanding the national grid becomes even more important. Whether you’re an eco-conscious consumer or a tech-savvy business owner, knowing how this system works can help you make informed decisions about your energy usage.
Read also:Best Remote Iot Monitoring With Raspberry Pi Your Ultimate Guide
What Exactly Is the National Grid?
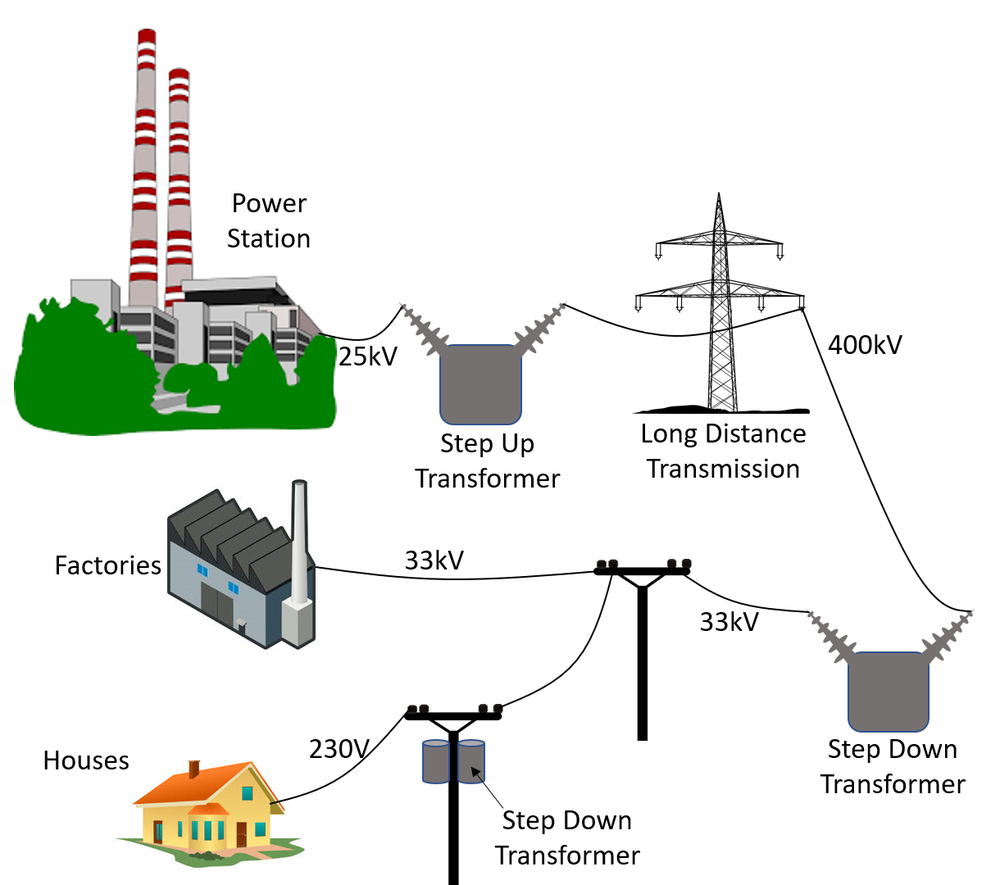
At its core, the national grid is a network of power lines, substations, and transformers that transmit electricity from power plants to end users. It’s like a highway system for electrons, designed to move electricity efficiently across vast distances. The grid is divided into different sections, each serving specific regions or cities, but they’re all interconnected to ensure a steady flow of power.
In the U.S., for example, the national grid is actually composed of three main interconnections: the Eastern Interconnection, the Western Interconnection, and the Texas Interconnection. These interconnections work together to balance energy supply and demand across the country. But don’t let the name fool you—national grids exist in many countries around the world, each with its own unique challenges and solutions.
How the National Grid Works
Here’s the simplified version: electricity is generated at power plants—whether they’re fueled by coal, natural gas, nuclear energy, or renewables like wind and solar. Once generated, the electricity is sent through high-voltage transmission lines to substations, where the voltage is stepped down to safer levels for distribution to homes and businesses. It’s a complex process that involves a lot of moving parts, but the end result is power that’s available at the flip of a switch.
One of the coolest things about the national grid is its ability to balance supply and demand in real-time. If one region is using more electricity than it’s producing, the grid can reroute power from another region to meet the demand. This flexibility is key to keeping the lights on, even during peak usage times like hot summer afternoons or cold winter nights.
The Evolution of the National Grid
The national grid as we know it today has come a long way since its early days. Back in the late 1800s, electricity was still a novelty, and power was generated and distributed locally. But as demand grew, so did the need for a more efficient and interconnected system. By the mid-20th century, the national grid had evolved into the massive network we rely on today.
Over the years, advancements in technology have transformed the national grid. From the introduction of high-voltage transmission lines to the development of smart grid technologies, the system has become more efficient, reliable, and sustainable. And with the rise of renewable energy sources like wind and solar, the grid is evolving once again to accommodate a cleaner, greener future.
Read also:Mastering Remoteiot Vpc Ssh On Raspberry Pi Download Windows 10 Free And Secure Your Setup
Challenges Facing the National Grid
While the national grid is a remarkable achievement, it’s not without its challenges. One of the biggest issues is aging infrastructure. Many parts of the grid were built decades ago and are in need of upgrades to keep up with modern demands. This can lead to power outages, inefficiencies, and even safety risks.
Another challenge is the integration of renewable energy sources. While renewables are great for the environment, they can be unpredictable. Solar panels don’t work at night, and wind turbines depend on, well, wind. The grid needs to adapt to these fluctuations and ensure a stable supply of power, even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
Key Components of the National Grid
To really understand the national grid, you need to know its key components. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Power Plants: Where electricity is generated using various energy sources.
- Transmission Lines: High-voltage lines that carry electricity over long distances.
- Substations: Facilities that step down the voltage of electricity for safe distribution.
- Distribution Lines: Lower-voltage lines that deliver electricity to homes and businesses.
- Smart Meters: Devices that allow consumers to monitor their energy usage in real-time.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring that electricity flows smoothly from power plants to end users. Without them, the grid wouldn’t function as efficiently or reliably as it does today.
Renewable Energy and the National Grid
As the world moves toward a more sustainable future, renewable energy is playing an increasingly important role in the national grid. Solar, wind, and other renewable sources are being integrated into the system to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. But this transition isn’t without its challenges.
One of the biggest hurdles is energy storage. Since renewables depend on natural conditions, they can’t always produce electricity when it’s needed. That’s where battery storage comes in—allowing excess energy to be stored and used during times of high demand. As technology improves, we can expect to see more advanced storage solutions that make renewable energy even more reliable.
Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grid technologies are revolutionizing how we manage and distribute electricity. By incorporating digital communication and automation, smart grids can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance reliability. For example, smart meters allow consumers to track their energy usage in real-time, helping them make more informed decisions about how and when they use power.
Another benefit of smart grids is their ability to detect and respond to issues quickly. If a power line goes down or a transformer fails, the system can automatically reroute power to minimize disruptions. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces the workload on utility workers.
The Economic Impact of the National Grid
The national grid is more than just a technical marvel—it’s a vital component of the global economy. Reliable access to electricity is essential for businesses, industries, and households alike. Without a stable grid, economic growth would grind to a halt.
Investing in the national grid also creates jobs and stimulates local economies. From engineers and technicians to construction workers and maintenance crews, the grid supports a wide range of careers. And as the grid continues to evolve, new opportunities are emerging in fields like renewable energy, energy storage, and smart grid technologies.
Environmental Benefits
One of the most significant benefits of the national grid is its potential to reduce environmental impact. By integrating renewable energy sources and improving efficiency, the grid can help lower greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. This is especially important as the world faces growing concerns about global warming and its effects on the planet.
Of course, achieving these benefits requires a commitment to innovation and collaboration. Governments, businesses, and consumers all have a role to play in creating a cleaner, greener grid that meets the needs of future generations.
Case Studies: National Grid in Action
Let’s take a look at some real-world examples of the national grid in action. In the U.S., the grid has successfully integrated large amounts of renewable energy into its system, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering emissions. Similarly, countries like Germany and Denmark have made significant strides in adopting renewable energy sources, thanks in part to their advanced grid infrastructure.
But it’s not just about developed nations. In developing countries, the national grid is helping to bring electricity to remote and underserved communities. Microgrids and off-grid solutions are also playing a crucial role in expanding access to power in areas where traditional infrastructure isn’t feasible.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the national grid is poised for even more innovation. Advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technology are paving the way for smarter, more efficient grids. These technologies can help optimize energy distribution, improve grid resilience, and enhance cybersecurity.
Another exciting trend is the rise of community-based energy projects. These initiatives allow local communities to generate and share their own electricity, reducing dependence on centralized power plants. As more people embrace this decentralized approach, the grid will continue to evolve in ways we can only imagine.
Conclusion: Why the National Grid Matters
In conclusion, the national grid is an essential part of modern life. It powers our homes, businesses, and industries, and it’s critical to the global economy and environment. While it faces challenges like aging infrastructure and the integration of renewables, the grid is evolving to meet these challenges head-on.
As consumers, we can all play a role in supporting a cleaner, more sustainable grid. By using energy-efficient appliances, investing in renewable energy, and advocating for policies that promote grid modernization, we can help create a brighter future for everyone. So the next time you flip a switch or charge your phone, take a moment to appreciate the incredible system that makes it all possible.
And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family! The more people understand the national grid, the better equipped we’ll be to tackle the challenges of tomorrow. Together, we can build a more sustainable, resilient, and equitable energy future.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is the National Grid?
- How the National Grid Works
- The Evolution of the National Grid
- Key Components of the National Grid
- Renewable Energy and the National Grid
- The Economic Impact of the National Grid
- Case Studies: National Grid in Action
- Future Trends
- Environmental Benefits
- Conclusion: Why the National Grid Matters